
Greenhouse gas concentrations hit new record
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) have released their annual Greenhouse Gas Bulletin which described the state of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, based on Global observations through to 2016.
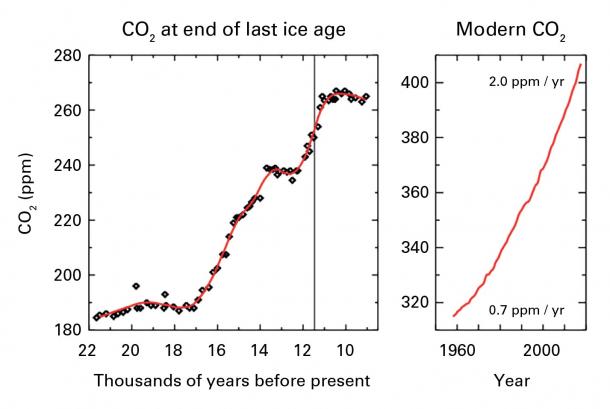
The bulletin reports that concentrations of carbon dioxide (CO₂) in the atmosphere surged at a record-breaking speed in 2016 to the highest level in 800,000 years – with Globally averaged concentrations of CO₂ reaching 403.3 parts per million in 2016, up from 400.00 ppm in 2015. Concentrations of CO₂ are now 145% of pre-industrial (before 1750) levels.
This is due to a combination of human activities (population growth, intensified agricultural practices, increased land use and deforestation, industrialisation and associated energy use from fossil fuel sources) as well as a strong El Niño event.
“Without rapid cuts in CO₂ and other greenhouse gas emissions, we will be heading for dangerous temperature increases by the end of this century, well above the target set by the Paris climate change agreement,” said WMO Secretary-General Petteri Taalas.
“CO₂ remains in the atmosphere for hundreds of years and in the oceans for even longer. The laws of physics mean that we face a much hotter, more extreme climate in the future. There is currently no magic wand to remove this CO₂ from the atmosphere,” said Mr Taalas.
The last time the Earth experienced a comparable concentration of CO₂ was 3-5 million years ago, when the temperature was 2-3°C warmer and sea level was 10-20 meters higher than it is now.